‘Call of Duty’ voice actors spent the summer on video calls like the rest of us
“Man, you died a lot of ways today,” he’d say.
“I don’t know why they killed me so bad,” Cowles would reply.
Such were the unusual conditions for Cowles and others when recording the dialogue — and other vocalizations — for the upcoming game “Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War,” the newest addition to the famed and fanciful war sim series. The blanket-draped fort served as the actress’s workstation, with a host of audio producers providing directions via video conference. Occasionally those instructions included imagining a wide variety of fates for her character, requiring lengthy sessions capturing death cries. All of it was part of a months-long, pandemic-related process to produce the game, one that proved both challenging in its never-before-done nature and cathartic for its ample opportunities to exorcise the many anxieties of 2020.
“It just felt so good to scream for that long,” said Cowles, who plays MI-6 operative Helen Park and supplied the character’s voice for both the game’s story and multiplayer modes. She recalled one session in which the game’s audio producers recorded her falling from a 30-story building. “I was like, ‘can we make it 40 floors? I could really use the extra 10 [stories] of just straight screaming.’ It just felt like a real relief.”
The unorthodox routine was shared by “Cold War’s” cast of 125 actors as they pivoted to follow safety protocols related to the novel coronavirus, which temporarily shut down the game’s production in March. The latest installment in the Call of Duty franchise, releasing Nov. 13, was completed with both developers and actors working remotely and overcoming a variety of logistical challenges.
“At the time [in March, when covid cases escalated in the United States] we thought it might be like 20 people or 50 percent of the studio who would have to work from home, and maybe that would be for like two weeks,” Dan Vondrak, Senior Creative Director at Raven Software, said. “And then it was everybody. … In my head, I was thinking, if this thing lasts six to eight weeks, we can’t get it done. That’s impossible.”
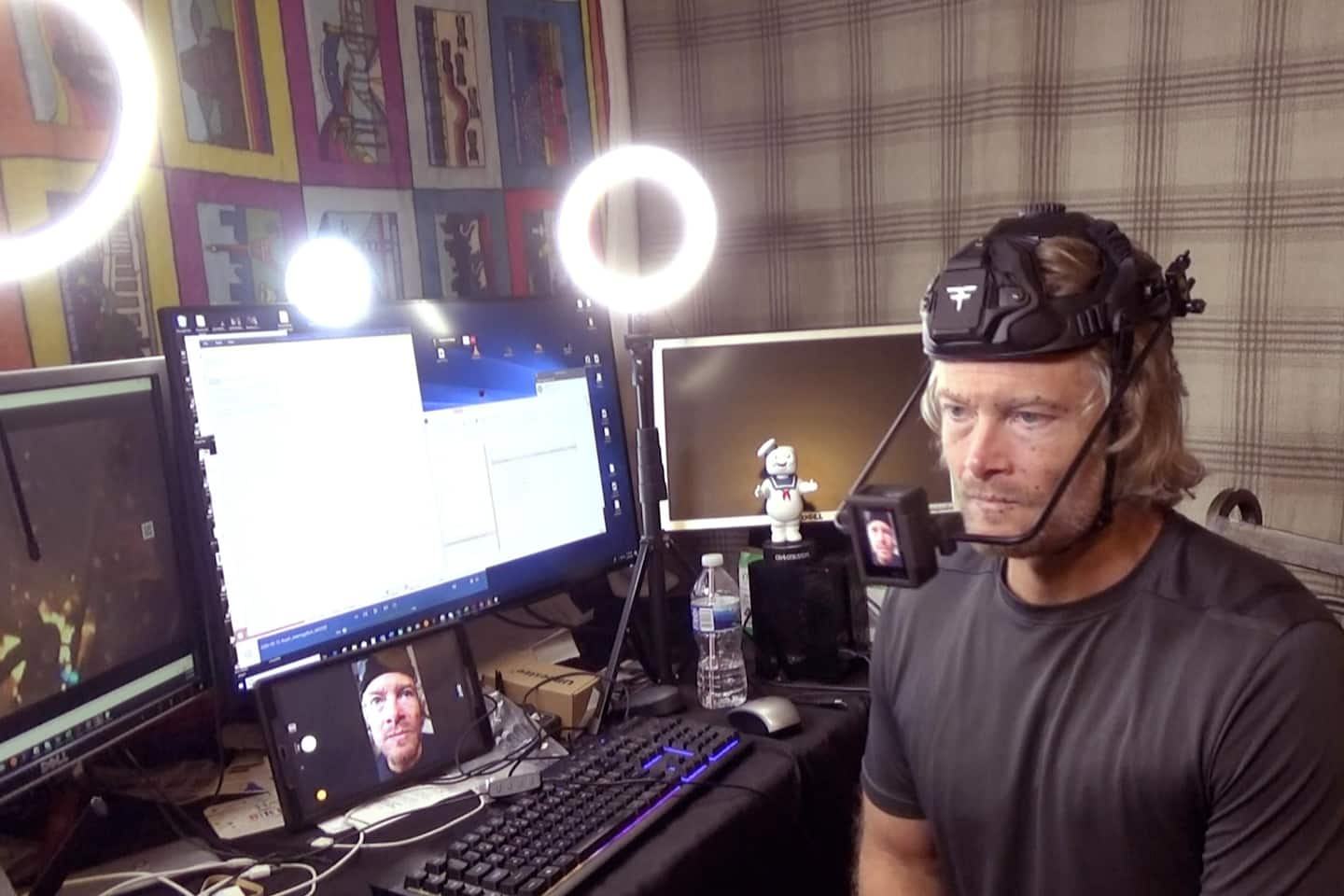
For Cowles and the game’s other actors, that meant recording lines of dialogue — and their many screams — from the confines of their homes. That process normally would be captured in large part during live shoots using motion capture suits on a studio sound stage. During the pandemic, capturing those recordings provided a unique challenge for narrative producer Natalie Pohorski and her team.
“One of those areas I thought we were just dead in the water was the external talent [voice overs],” Vondrak said. “I can’t have actors go into a studio. So, how is this going to work? And what Natalie and the narrative team did to get that to work and have people recording at home was unbelievable.”
Before dispersing from the studio, Pohorski and Vondrak estimated they had between 50 and 60 percent of the voice over work finalized. Working with their partners at Activision (the game’s publisher) and Treyarch (“Cold War’s” co-developer), Pohorski and her team shipped the actors crates filled with recording equipment that included helmets wired with microphones, sound mixing boards and materials to improve the acoustics around their homes.
“They sent me this giant Pelican briefcase that looked like I’m an arms dealer,” Cowles said.
Veteran actor Bruce Thomas, who plays the role of CIA agent Russell Adler in the game, already had a 5-foot-by-5-foot sound booth he’d constructed in his apartment adjacent to his kitchen. He’d used it to previously to record voice overs, including for some commercials, but he’d never recorded himself there quite so regularly — or at quite the same volume level. To that end, he sought to get ahead of any potential problems with a kind gesture and a heads-up for his neighbors about any yells they may hear through the walls.
“I delivered cookies and a little note to their doors right next to me and below me,” Thomas said. “I just moved here in January, so I hadn’t really met them yet, and I got a text message from the person below me who was like, ‘Oh my God! You do that for a living? How cool is that? Even if I hear you, don’t worry about it.’”
The conditions also required the actors to perform another role as well: that of audio engineer, recording and tinkering with sound levels to ensure quality and consistency. The studio’s engineers would call actors and walk them through proper setups and troubleshoot issues, but when something went wrong, the actors would have to be the ones to fix it manually. Turns out CIA operatives have the same tech troubles as other remote workers.
“Because of covid, everybody’s home and sharing bandwidth,” Thomas said about the Internet connection in his apartment building. “Sometimes it would just cut right out [during an online recording session]. And sometimes when that happens, a glitch will happen on your laptop and so you have to reboot it.”
The recording process consisted of four sessions per day, every day of the week, according to Pohorski, who also noted they wrapped at a similar time compared to what they’d anticipated in their pre-pandemic production schedule, even as they navigated challenges that would have been easily addressed in their usual studio setting.
“To not be able to just walk up and touch the screen and act out what I was talking about … ‘I want the guy’s head to turn this way,’ … I was trying to do it real time in a video camera,” Vondrak said. “Just the communication of that last 20 percent [of the game] was probably the most difficult.”
The on-the-fly evolution of several standardized processes did carry some fringe benefits, according to both the developers and actors. On the development team, Vondrak noted some people seemed more willing to contribute their opinions to the creative process when they didn’t feel the pressure of speaking up in a formal meeting. For the actors, Cowles said her isolated, remote location led her to take more chances with her character.
“I think I was able to make facial expressions and noises that, in a normal setting, my body would be like, ‘Don’t, don’t, don’t. You don’t want to make that noise. Don’t make that face,’” Cowles said. “But I was alone in this thing, and you know, the context in which we’re working [as characters] is this crazy war zone where horrible things are going down. Right? And no one in that situation is thinking about the sound they’re making or the face that they’re making. … I think that led to a degree of authenticity in my work.”
Another silver lining, according to Vondrak, was the increased flexibility in scheduling follow-up sessions for VO work. Oftentimes VO recording sessions are pegged to specific times of the year when the developers can gather all the actors in one place and free them from their other projects. (For example, Thomas is also the motion capture actor for Master Chief for the upcoming game “Halo: Infinite.”) With everyone working from home, the actors’ schedules became more flexible.
“It was like, wait a minute, we can just go back to these people and have them pop out of their family room, into their closet and record some VO lines,” Vondrak said. “Normally it would have been like, ‘We need some new lines.’ And [the schedulers] would have said, ‘Well, the next pick up session where everyone’s going to be in the studio is June.’ It’s [normally] a very slow, formal process.”
The flexibility did carry an occasional side effect of home life encroaching on the working world, and vice versa, often providing a uniquely 2020 kind of amusement.
Cowles remembered recording a scene in which her character laments the loss of one of her companions, screaming his name repeatedly as a helicopter whisks her away.
“I came out of the sewing room, and my boyfriend is like … ‘So, who is he?’” Cowles said. “I was like, ‘Don’t worry about it. He’s dead now.’”
Read more: